USES OF NODAL ANALYSIS :
It is an important technique to finding solution in a network
ABOUT NODE :
Three or more branches connected at a point is called as node point or node.
STEPS INVOLVES IN NODAL ANALYSIS :
STEP - 1 : Find the all nodal points and choose one point as a reference point.
STEP - 2 : Label the node voltage and mark current.
STEP - 3 : Apply Kirchhoff's current law at node point.
NOTE :
Node voltage is obtain by below pneumatics.
Node voltage = Voltage at arrow tail - Voltage at arrow head
APPLICATION OF NODAL ANALYSIS :
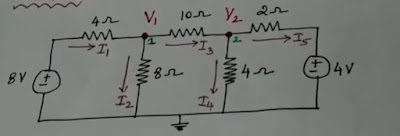
Determine the current through 10 ohm resistor.
STEP - 1 : There are three nodal point in the above circuit.
STEP - 2 :Mark the nodal point and current.
STEP - 3 : Apply Kirchhoff's current law at each node point.
At Node V1 :
I1 - I2 - I3 = 0 -----> 1
Get the value of current refer notes,
I1 = 8 - V1/4 , I2 = V1 - 0/8 , I3 = V1 - V2/10
Substitute the current value in equation 1
((8 - V1)/4) - (V1/8) - ((V1 - V2)/10) =0
0.475 V1 - 0.1 V2 = 2 ------> 2
At Node V2 :
I3 - I4 - I5 =0 ------> 3
Get the value of current refer notes,
I3 = V1 - V2/10 , I4 = V2 - 0/4 , I5 = V2 - 4/2
Substitute the value of current in the equation 3
((V1 - V2)/10) - ((V2 - 0)/4) - ((V2 - 4)/2) = 0
0.1 V1 - 0.85 V2 = -2 ------> 4
Solving the equation 2 and 4, we get
V1 = 4.825 V , V2 = 2.920 V
For the current at 10 ohm,
I10 ohm = ((V1-V2)/10) = ((4.825 - 2.920)/10) = 1.905/10 = 0.1905 ohm.
IN THIS WAY WE USE THE NODAL ANALYSIS.